Understanding Septic Tank Sizing
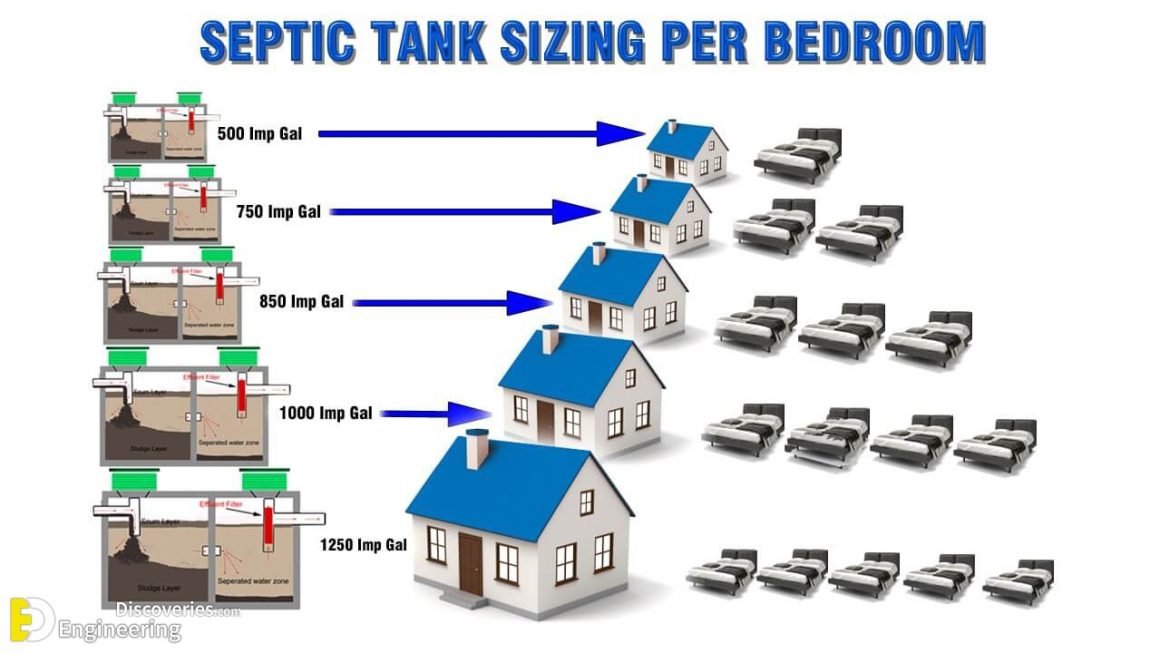
A septic tank is an essential component of a home’s wastewater management system, playing a crucial role in treating and disposing of sewage. Choosing the right size for your septic tank is vital for ensuring its efficient operation and preventing costly problems down the line.
Factors Influencing Septic Tank Size
Several factors influence the required size of a septic tank, including the number of bedrooms, the size of your household, and the overall water usage. These factors determine the amount of wastewater your system needs to handle.
Septic Tank Size Guide
The table below provides a general guide to septic tank sizes based on the number of bedrooms in a home. This is a common starting point for sizing, but individual needs may vary.
| Number of Bedrooms | Typical Tank Capacity (gallons) | Recommended Usage |
|—|—|—|
| 1-2 | 750-1000 | 1-2 people |
| 3-4 | 1000-1500 | 3-4 people |
| 5+ | 1500+ | 5+ people |
Consequences of Incorrect Septic Tank Sizing
Undersized Septic Tank
An undersized septic tank can lead to various problems, including:
- Frequent backups: The tank overflows, leading to sewage backups in your home or yard.
- Reduced treatment efficiency: The wastewater doesn’t have enough time to settle properly, leading to the discharge of untreated solids into the leach field.
- Premature failure: The tank is constantly overloaded, leading to premature wear and tear.
Oversized Septic Tank
While an oversized tank may seem like a good idea, it can also have drawbacks:
- Increased cost: Larger tanks are more expensive to install and maintain.
- Slower treatment: Wastewater sits in the tank for longer, potentially leading to odor problems.
- Reduced efficiency: The tank may not be operating at its optimal capacity, leading to inefficient treatment.
Factors Affecting 2-Bedroom Septic Tank Size: 2 Bedroom Septic Tank Size
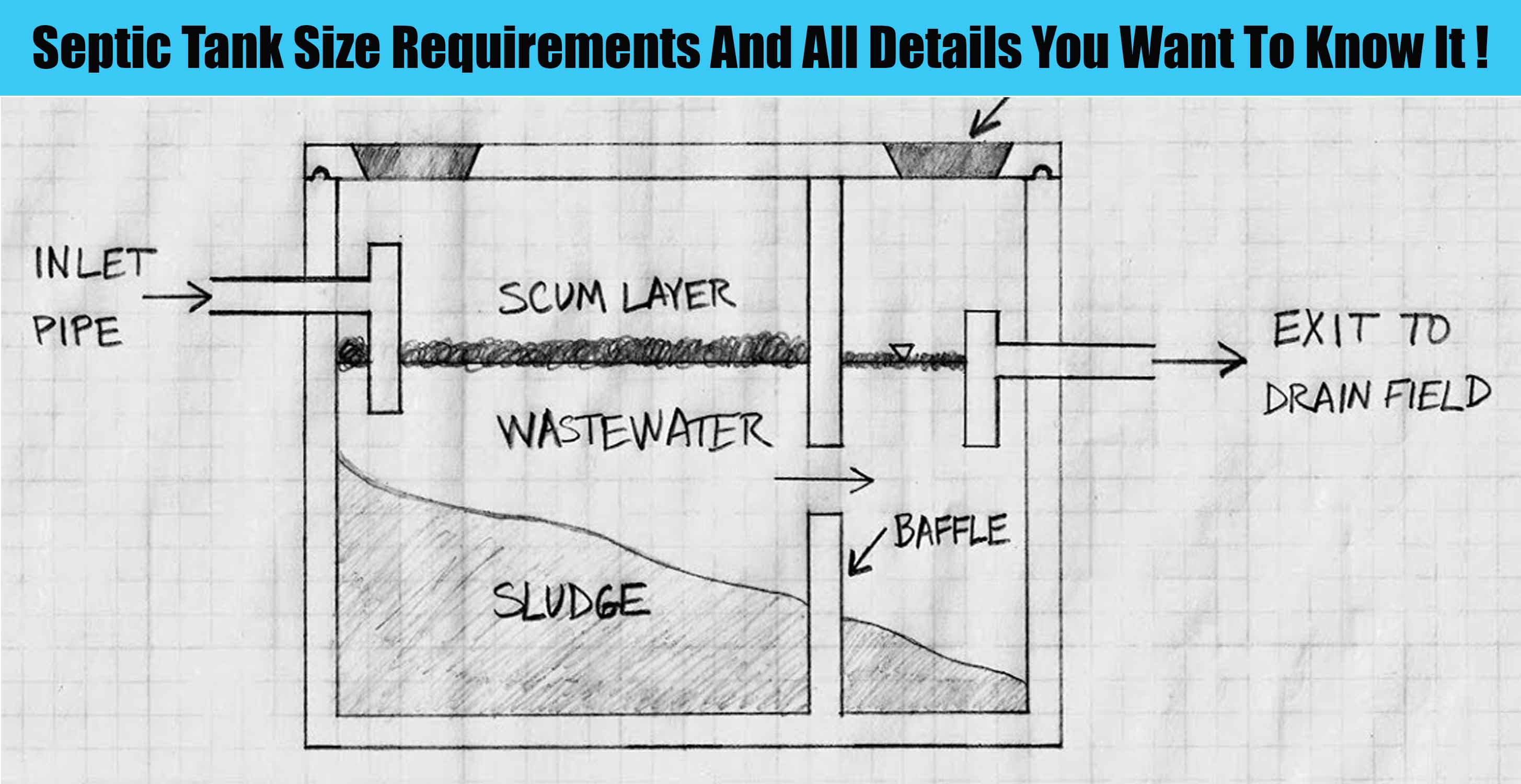
The size of a septic tank for a 2-bedroom home is not a fixed number. It depends on several factors, including the number of people living in the house, their water usage habits, the type of soil, and local regulations.
Water Usage Patterns
Water usage patterns play a significant role in determining the appropriate septic tank size. A 2-bedroom home with a family of four who use water conservatively will require a smaller septic tank compared to a home with two people who frequently use water-intensive appliances like dishwashers and washing machines.
- Higher Water Consumption: Homes with more occupants or those with water-intensive appliances like dishwashers, washing machines, and bathtubs require larger septic tanks to accommodate the increased wastewater volume.
- Lower Water Consumption: Homes with fewer occupants or those using water-saving appliances and practices can utilize smaller septic tanks.
Water-Saving Appliances and Practices
Water-saving appliances and practices can significantly reduce the amount of wastewater generated, thereby impacting the required septic tank size.
- Low-Flow Showerheads and Toilets: These appliances use less water per use, reducing the overall water consumption.
- Water-Efficient Washing Machines: Modern washing machines with water-saving features use less water per load, contributing to lower wastewater volume.
- Water-Saving Dishwashers: Dishwashers with water-efficient settings reduce water consumption during dishwashing.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater for gardening and other outdoor uses can significantly reduce the amount of water drawn from the municipal supply, lowering wastewater generation.
Soil Type and Local Regulations
The type of soil and local regulations can significantly influence septic tank sizing.
- Soil Type: Permeable soils, such as sandy loam, allow for efficient drainage, potentially requiring smaller septic tanks. Conversely, clay soils with poor drainage may require larger tanks to accommodate the slower wastewater filtration process.
- Local Regulations: Local building codes and regulations often specify minimum septic tank sizes based on factors such as the number of bedrooms, occupants, and the area’s wastewater treatment capacity.
Considerations for Septic Tank Installation
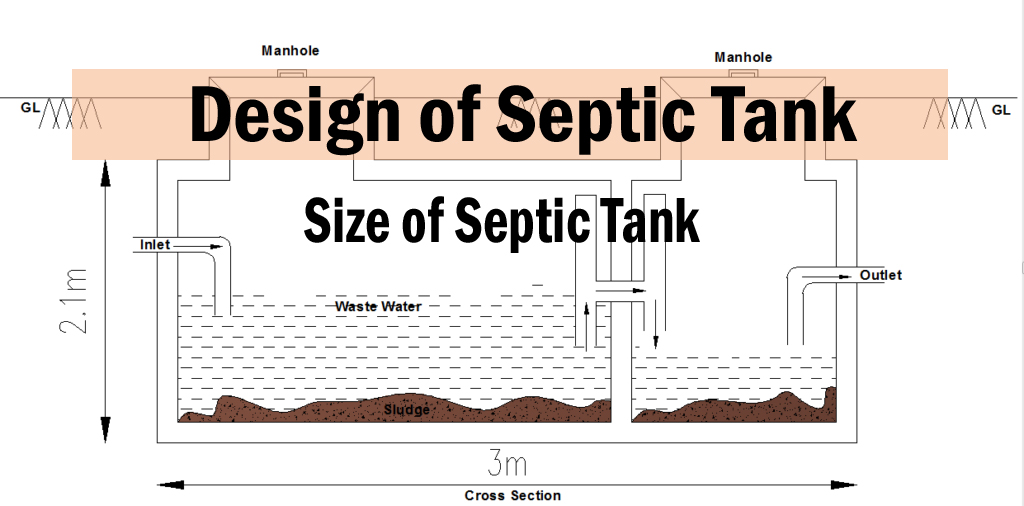
Installing a septic system is a significant investment, and it’s essential to approach the process thoughtfully to ensure proper functionality and longevity. This section delves into key considerations for septic tank installation, covering site evaluation, permitting, cost estimation, and a step-by-step guide for installation.
Site Evaluation
A thorough site evaluation is crucial before proceeding with septic tank installation. This assessment helps determine the suitability of the location, soil conditions, and potential environmental impacts.
- Soil Analysis: Understanding the soil type is essential for determining the absorption field’s effectiveness. Permeable soils allow for efficient drainage, while dense or clay-rich soils may require alternative solutions like sand mounds or raised beds.
- Topography: The slope of the land influences drainage patterns. A gentle slope is ideal for gravity-fed systems, while steeper slopes may require additional engineering considerations.
- Distance to Water Sources: Ensuring the septic system is a safe distance from wells, lakes, or streams is paramount to prevent contamination. Regulations vary by location, so consulting local authorities is crucial.
- Vegetation: Existing trees or large shrubs near the proposed site should be considered as their roots can potentially damage the septic system.
Permitting
Obtaining necessary permits is a crucial step in the septic tank installation process. These permits ensure compliance with local regulations and environmental standards.
- Contact Local Authorities: Reach out to your local building department or environmental agency to inquire about specific permit requirements for septic tank installation in your area.
- Submit Application: Prepare and submit the necessary application forms, including site plans, soil test reports, and other relevant documents.
- Inspection: Once the permit is granted, an inspector will visit the site to ensure compliance with regulations before installation begins.
Cost Estimation
The cost of septic tank installation varies depending on factors like tank size, soil conditions, and the complexity of the system.
- Tank Size: The size of the septic tank is directly related to the number of bedrooms and occupants. Larger tanks generally cost more.
- Soil Conditions: If the soil requires extensive excavation or specialized drainage solutions, the installation cost will increase.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs vary depending on location and the complexity of the installation process.
- Materials: The cost of materials, including the tank, pipes, and other components, can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Septic Tank Installation Guide, 2 bedroom septic tank size
Installing a septic tank requires careful planning and adherence to safety protocols. This step-by-step guide provides a general overview of the process.
Important Note: It is highly recommended to hire a qualified and experienced septic tank installer for the installation process. Attempting to install a septic tank without professional expertise can lead to safety hazards and potential system malfunctions.
- Excavation: A trench is dug for the tank and absorption field, ensuring proper depth and slope for drainage.
- Tank Placement: The septic tank is carefully placed within the excavated trench, ensuring proper leveling and support.
- Piping Connections: The inlet and outlet pipes are connected to the tank, ensuring proper sealing and watertight connections.
- Absorption Field Installation: The absorption field is installed, consisting of perforated pipes buried in trenches filled with gravel. This allows wastewater to filter through the soil.
- Backfill and Grading: The trenches are backfilled with soil, and the area is graded to ensure proper drainage away from the septic system.
- Inspection and Testing: Once the installation is complete, a qualified inspector will examine the system for compliance with regulations and ensure proper functionality.
Septic System Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term efficiency and longevity of your septic system.
- Pump-Outs: Septic tanks should be pumped out regularly to remove accumulated solids. The frequency of pump-outs depends on the size of the tank and the number of occupants. A general guideline is to pump out every 3-5 years.
- Inspections: Regular inspections by a qualified professional can identify potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs later. Inspections should include checking for leaks, cracks, and blockages in the tank and absorption field.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid flushing items like grease, oil, and non-biodegradable materials down the drain, as they can clog the system and lead to malfunctions.
